Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Photoelectric Effect, Stopping Potential for Photoelectrons, Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light & Secondary Electron Emission etc.
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5 V. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be:
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted would be
The maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is 3 eV. Its stopping potential is:
The maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is . Its stopping potential is
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation in terms of the stopping potential and the threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material is
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and .
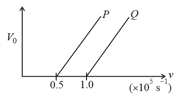
Which metal has
(i) a smaller threshold wavelength?
(ii) smaller kinetic energy?
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and :
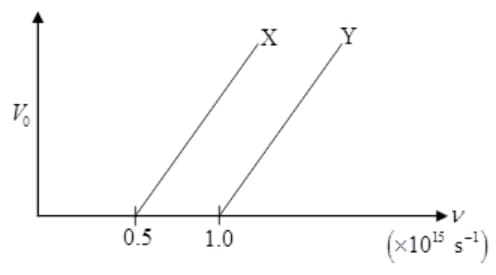
(i) Which of the metals has larger threshold wavelength? Give reason.
(ii) Explain, giving reason, which metal gives out electrons, having larger kinetic energy, for the same wavelength of the incident radiation.
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
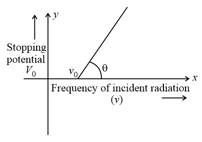
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
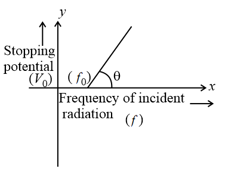
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
Show graphically how the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface varies with the frequency of the incident radiation.
In the photo-electron emission, the energy of the emitted electron is
The maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted in the photoelectric effect is linearly dependent on the________________ of the incident radiation.
A copper ball of radius and work function is irradiated with ultraviolet radiation of wavelength . The effect of irradiation results in the emission of electrons from the ball. Further the ball will acquire charge and due to this there will be a finite value of the potential on the ball. The charge acquired by the ball is :
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : Out of microwaves, infrared rays and ultraviolet rays, ultraviolet rays are the most effective for the emission of electrons from a metallic surface
Statement II : Above the threshold frequency, the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons is inversely proportional to the frequency of the incident light
In the light of above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
The difference between threshold wavelengths for two metal surfaces and having work function and in is:
{Given, }
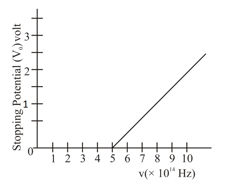
The variation of stopping potential as a function of the frequency of the incident light for a metal is shown in figure. The work function of the surface is
A metallic surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential is . If the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential becomes . The threshold wavelength for this metallic surface will be
